Emulating Android
This youtube playlist has really easy to follow instructions on how to get started with android hacking:
Android Hacking Youtube Playlist
Setting Up an Android Virtual Device
:: C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\emulator>
emulator.exe -list-avds
emulator.exe -avd <AVD_name>
:: Go to C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\platform-tools>
:: Make sure adb can "see" your device
adb.exe devices
:: should see something like:
:: List of devices attached
:: emulator-5554 offline
:: Get shell on android virtual device (AVD)
adb.exe shell
:: Push file from PC to AVD
adb.exe push
:: Pull file from AVD to PC
adb.exe pull
:: Example
adb.exe push C:\User\<username>\Desktop\test.txt /storage/self/primary
/storage/self/primary is the Downloads folder that can be accessed through the AVD UI.
With the AVD running, you can open a linux VM and connect to the AVD using adb (Android debugger).
sudo apt install adb
adb devices
# nothing should be listed
adb connect 10.0.2.2
The Android Emulator uses 10.0.2.2 as a "Special alias to your host loopback interface (127.0.0.1 on your development machine)"; see here.
Where to get APKs
Two primary places:
- https://apkpure.com/
- Note: not regulated, could contain malware
- Apk Extractor
- A regular app that you download from the Playstore. It lists all the apps stored on the phone and then you can "extract" them to an accessible location in the phone's file system. Then you can use
adb pullto get the APK on your host computer.
- A regular app that you download from the Playstore. It lists all the apps stored on the phone and then you can "extract" them to an accessible location in the phone's file system. Then you can use
Decompiling APKs
There's a couple tools you can use:
apktool
https://github.com/iBotPeaches/Apktool
sudo apt install apktool
apktool d <apk_file> # decompiles the apk file
jadx
https://github.com/skylot/jadx
sudo apt install jdx
jadx-gui
Installing a Burp Suite cert in an AVD
emulator.exe -avd <AVD_name> -writeable-system
Export the cert by going to Proxy > Options > "Import / export CA certificate"
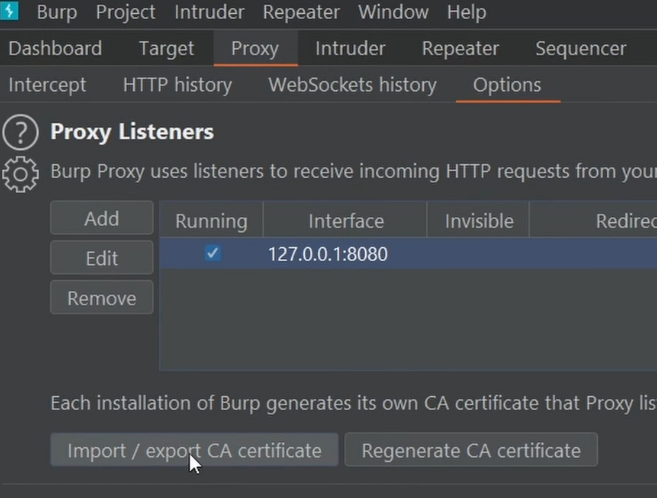
Export it in DER format.
On linux:
openssl x509 -inform DER -in burpcert.der -out burpcer.pem
FOO=$(openssl x509 -inform PEM -subject_hash_old -in burpcert.der | head -1)
mv burpcert.pem ${FOO}.0
adb push ${FOO}.0 /sdcard/
# now connect to AVD in root mode
adb root
# this won't work if you didn't start your AVD with -writeable-system flag
adb remount
adb shell
# NOW IN ADB SHELL
cd /sdcard/system/etc/security/cacerts/
mv <FOO.0 file from earlier> ./
chmod 644 <our cert> # run to match permissions of other certs in this dir
# now reboot device
Go into the AVD's settings app:
Security & location > Encryption & credentials > Trusted credentials
You should see "PortSwigger" in the list of certs.